| Numéro |
J. Phys. III France
Volume 3, Numéro 9, September 1993
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 1761 - 1767 | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/jp3:1993102 | |
J. Phys. III France 3 (1993) 1761-1767
High speed (
 GHz) InGaAs/InP avalanche photodiodes
grown by gas source molecular beam epitaxy with a thin quaternary grading
layer for high bit rate (
GHz) InGaAs/InP avalanche photodiodes
grown by gas source molecular beam epitaxy with a thin quaternary grading
layer for high bit rate (
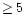 Gbit/s) systems
Gbit/s) systems
G. Ripoche1, J.-L. Peyre1, M. Lambert1 and S. Mottet2
1 Alcatel Alsthon Recherche, route de Nozay, 91460 Marcoussis, France
2 CNET, 2 route de Trégastel, 22300 Lannion, France
(Received 10 November 1992, revised 8 March 1993, accepted 9 March 1993)
Abstract
High speed InGaAs/InP avalanche photodiodes (APD) grown by gas source molecular
beam epitaxy (GSMBE) for high bit rate (
![]() Gbit/s) optical communications
systems have been successfully processed. As predicted by modelling, a thin quaternaty
grading layer practically suppresses "hole pile up" at the InGaAs/InP hetero-interface.
Devices with bandwidth over 6 GHz, gain-bandwidth product in excess of 50 GHz,
low dark current and excellent stability have been achieved with a high fabrication yield.
Gbit/s) optical communications
systems have been successfully processed. As predicted by modelling, a thin quaternaty
grading layer practically suppresses "hole pile up" at the InGaAs/InP hetero-interface.
Devices with bandwidth over 6 GHz, gain-bandwidth product in excess of 50 GHz,
low dark current and excellent stability have been achieved with a high fabrication yield.
Résumé
Des photodiodes à avalanche (PDA) InGaAs/InP rapides pour communications optiques
à haut débit (
![]() Gbit/s) ont été réalisées sur des hétérostructures élaborées
par épitaxie par jets moléculaires à sources gaz (EJM-SG). Conformément aux
indications de la modélisation, une fine couche quaternaire de transition a
permis d'éviter le " stockage " des trous à l'interface InGaAs/InP. Des PDA
ayant une bande passante et un produit gain
Gbit/s) ont été réalisées sur des hétérostructures élaborées
par épitaxie par jets moléculaires à sources gaz (EJM-SG). Conformément aux
indications de la modélisation, une fine couche quaternaire de transition a
permis d'éviter le " stockage " des trous à l'interface InGaAs/InP. Des PDA
ayant une bande passante et un produit gain
![]() bande passante respectivement
supérieurs à 6 GHz et à 50 GHz, un faible courant d'obscurité et présentant
une excellente stabilité, ont été obtenues avec un rendement de fabrication élevé.
bande passante respectivement
supérieurs à 6 GHz et à 50 GHz, un faible courant d'obscurité et présentant
une excellente stabilité, ont été obtenues avec un rendement de fabrication élevé.
© Les Editions de Physique 1993



